Document
Multifocal skin fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in a patient with a large abdominal mass.
Other titles
امتصاص متعدد البؤر للفلوروديوكسي جلوكوز في جلد مريض لديه كتلة كبيرة في البطن
Publisher
College of Medicine, Sultan Qaboos University.
Gregorian
2018-08
Language
English
Subject
English abstract
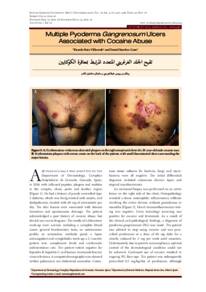
A 30-year-old male patient presented to the emergency room of a community hospital in California, USA, in 2018 with lower abdominal pain. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) revealed a 9-cm mass in the left adrenal gland. Subsequently, the patient became very anxious and stressed and developed chest and abdominal pain, which resulted in more than 10 emergency room visits over the next few months. The pain reportedly subsided once the patient was prescribed benzodiazepine. He was then referred to the Ronald Reagan University of California Los Angeles Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, for management of the mass. At referral, the patient was currently taking esomeprazole and lorazepam. His past medical history included mild hypertension, obesity and kidney stones. Multiple family members had a history of malignancy. A physical examination indicated tachycardia and multiple acne lesions on the back. Biochemical tests revealed normal levels of catecholamines, metadrenalines, aldosterone, renin, potassium, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and cortisol. Various emotional states such as stress, anger, anxiety and fear increase blood flow to the facial skin. In the present case, the patient was under extreme stress due to the recent diagnosis of a potentially malignant abdominal mass and was very anxious during the FDG-PET procedure. However, upon physical examination, his facial skin appeared completely\ normal. It is therefore likely that the diffuse facial skin FDG uptake was due to emotional stress. While it is unknown if emotional stress can cause hyperaemia in the chest and abdominal skin, FDG uptake in these areas was normal. This case illustrates that multifocal skin FDG uptake can be due to benign lesions in patients with suspected malignancies and that diffuse facial skin FDG uptake may be due to emotional stress.
Member of
Resource URL
Citation
Yu, Run (2018). Multifocal Skin Fluorodeoxyglucose Uptake in a Patient with a Large Abdominal Mass. Sultan Qaboos University Medical Journal, 18 (3), e405–406.
Arabic abstract
قدم مريض يبلغ من العمر 30 عامًا إلى غرفة الطوارئ في مستشفى مجتمعي في كاليفورنيا ، الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية ، في عام 2018 يعاني من آلام أسفل البطن. كشف التصوير المقطعي للبطن عن كتلة 9 سم في الغدة الكظرية اليسرى. بعد ذلك ، أصبح المريض شديد القلق والتوتر وأصاب بألم في الصدر والبطن ، مما أدى إلى أكثر من 10 زيارات لغرفة الطوارئ خلال الأشهر القليلة المقبلة. وبحسب ما ورد خف الألم بمجرد وصف المريض للبنزوديازيبين. ثم تمت إحالته إلى مركز لوس أنجلوس الطبي بجامعة رونالد ريغان في كاليفورنيا ، لوس أنجلوس ، كاليفورنيا ، لإدارة الكتلة. عند الإحالة ، كان المريض يأخذ حاليًا إيزوميبرازول ولورازيبام. تضمن تاريخه الطبي السابق ارتفاع ضغط الدم الخفيف والسمنة وحصى الكلى. كان لدى العديد من أفراد الأسرة تاريخ من الأورام الخبيثة. أظهر الفحص البدني عدم انتظام دقات القلب وآفات حب الشباب المتعددة على الظهر. كشفت الاختبارات البيوكيميائية عن مستويات طبيعية من الكاتيكولامينات والميتادرينالين والألدوستيرون والرينين والبوتاسيوم وكبريتات ديهيدرو إيبي أندروستيرون والكورتيزول. حالات عاطفية مختلفة مثل التوتر والغضب والقلق والخوف تزيد من تدفق الدم إلى بشرة الوجه. في الحالة الحالية ، كان المريض تحت ضغط شديد بسبب التشخيص الأخير لكتلة بطنية يحتمل أن تكون خبيثة وكان قلقًا جدًا أثناء إجراء FDG-PET. ومع ذلك ، بعد الفحص البدني ، بدت بشرة وجهه طبيعية تمامًا. لذلك من المحتمل أن يكون امتصاص جلد الوجه المنتشر FDG بسبب الإجهاد العاطفي. في حين أنه من غير المعروف ما إذا كان الإجهاد العاطفي يمكن أن يتسبب في احتقان في الصدر وجلد البطن ، كان امتصاص FDG في هذه المناطق طبيعيًا. توضح هذه الحالة أن امتصاص الجلد متعدد البؤر FDG يمكن أن يكون بسبب الآفات الحميدة في المرضى الذين يشتبه في إصابتهم بأورام خبيثة وأن امتصاص جلد الوجه المنتشر FDG قد يكون بسبب الإجهاد العاطفي.
Category
Journal articles